Oncodheep


Contact Us
For more information. Please complete this form.

Services
Home | Services
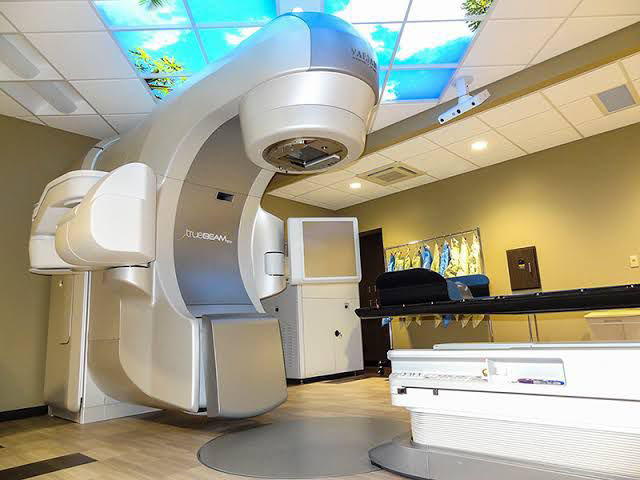
Radiation Oncology ?
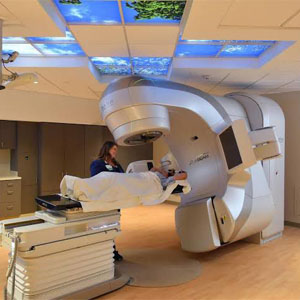
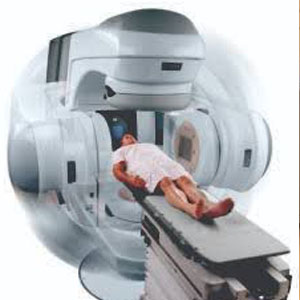
Radiation oncology is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on the use of ionizing radiation to treat cancer and certain non-cancerous conditions. The primary goal is to destroy cancer cells while sparing the surrounding normal tissues as much as possible. This is achieved using various advanced technologies and techniques.
Key Components of Radiation Oncology
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)
- Delivers high-energy X-rays, electrons, or protons to the tumor from outside the body.
Techniques include
- 3D Conformal Radiotherapy (3D-CRT)
- Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT).
- Image-Guided Radiotherapy (IGRT).
- Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT).
- Proton Therapy.
Brachytherapy
- Involves placing radioactive sources directly inside or near the tumor.
- Common in treating cervical, prostate, breast, and head-and-neck cancers.
- Techniques include High-Dose-Rate (HDR), Low-Dose-Rate (LDR), and Permanent Seed Implants.
Systemic Radiation Therapy
- Uses radioactive substances, such as radioiodine or radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies, administered orally or intravenously.
Role of a Radiation Oncologist
- Develops and oversees the patient’s radiation treatment plan.
- Collaborates with medical oncologists and surgeons in multidisciplinary cancer care.
- Ensures precise delivery of radiation to maximize tumor control and minimize side effects.
Advancement in Radiation oncology
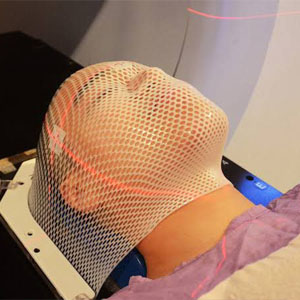
Image-Guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT)
- Overview: Combines imaging technologies with radiation delivery to ensure accurate targeting of the tumor.
- Utilizes CT, MRI, or ultrasound before or during treatment.
- Accounts for tumor motion caused by breathing or other physiological factors.
- Common in treating lung, prostate, and abdominal cancers.
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
- Overview: Delivers precise radiation doses by modulating the intensity of radiation beams.
- Spares surrounding normal tissues better than conventional techniques.
- Effective for tumors near critical organs (e.g., head and neck, pelvic cancers).
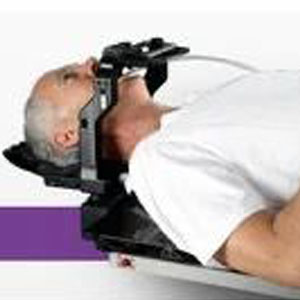
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
- SRS: A single high-dose radiation session, often for brain tumors or AVMs.
- SBRT: Delivers high-dose radiation over 1–5 sessions to extracranial tumors (lung, liver, spine).
- Highly precise, uses advanced immobilization and imaging.
- Ideal for small, well-defined tumors.
Proton Beam Therapy (PBT)
- Overview: Uses protons instead of photons for radiation therapy.
- Delivers maximum dose to the tumor while sparing deeper tissues.
- Beneficial for pediatric cancers, spinal tumors, and tumors near critical structures.
- Emerging Techniques.
- FLASH Proton Therapy: Extremely high-dose rate with reduced side effects.
Adaptive Radiotherapy (ART)
- Overview: Adjusts treatment plans in response to changes in tumor size, shape, or patient anatomy during the treatment course.
- Improves precision in dynamic situations (e.g., weight loss, tumor shrinkage).
- Beneficial for pediatric cancers, spinal tumors, and tumors near critical structures.
- Often used with advanced imaging (e.g., MRI-LINAC).
Total Marrow Irradiation (TMI)
- Overview: A specialized form of total body irradiation (TBI), sparing non-marrow tissues.
- Used as conditioning therapy before bone marrow transplantation.
- Reduces complications in hematologic cancers.
Radiopharmaceuticals and Molecular Radiotherapy
- Overview: Systemic administration of radioactive substances targeting specific molecules.
- Examples:Radioiodine (I-131): For thyroid cancer.
- Radium-223: For metastatic prostate cancer.
- Lutetium-177 PSMA: For advanced prostate cancer.
- Theranostics: Combines diagnostic imaging and therapy.
Brachytherapy Innovations
- Advancements:Image-guided (ultrasound, CT, MRI) brachytherapy for precise source placement.
- 3D printing for custom applicators.
- Combination therapies with external beam radiation for complex cases.
These techniques collectively aim to enhance treatment efficacy, improve survival rates, and reduce complications, representing the future of radiation oncology.
Working Time
-
Mon - Tue-10:00 – 18:00
-
Wed - Thu-10:00 – 17:00
-
Fri-Sat-10:00 – 12:30
-
Sun-Closed
Need a personal health plan?

Dr.Dheepika B
Radition Oncology
+91 81221 70915